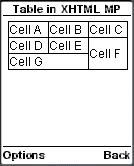
To create a table in XHTML MP, you need the <table>, <tr> and <td> tags. Data in a cell is enclosed in <td></td> tags. Cells in the same row are enclosed in <tr></tr> tags. All rows are enclosed in <table></table> tags. So, <td></td> should be enclosed in <tr></tr> and <tr></tr> should be enclosed in <table></table>. The following XHTML MP example demonstrates how to create tables:
<?xml version=”1.0″?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC “-//WAPFORUM//DTD XHTML Mobile 1.0//EN” “http://www.wapforum.org/DTD/xhtml-mobile10.dtd”>
<html xmlns=”http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml”>
<head>
<title>Table in XHTML MP</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Cell A</td>
<td>Cell B</td>
<td>Cell C</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell D</td>
<td>Cell E</td>
<td rowspan=”2″>Cell F</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan=”2″>Cell G</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
The result of the above XHTML MP markup code in mobile phone emulators is shown below:
|
|
WAP CSS is required to control the presentation aspect of a table. For example, if you want to add a border to the table or specify the color of a table cell, you have to make use of WAP CSS. To let you see clearly the effect of the rowspan and colspan attributes in the previous XHTML MP example, we specify black borders to the table cells with the WAP CSS border property, like this:
td {
border: thin solid black
}
|
|