Sharding cluster介绍
这是一种可以水平扩展的模式,在数据量很大时特给力,实际大规模应用一般会采用这种架构去构建monodb系统。
要构建一个 MongoDB Sharding Cluster,需要三种角色:
Shard Server: mongod 实例,用于存储实际的数据块,实际生产环境中一个shard server角色可由几台机器组个一个relica set承担,防止主机单点故障
Config Server: mongod 实例,存储了整个 Cluster Metadata,其中包括 chunk 信息。
Route Server: mongos 实例,前端路由,客户端由此接入,且让整个集群看上去像单一数据库,前端应用可以透明使用。
Sharding架构图:
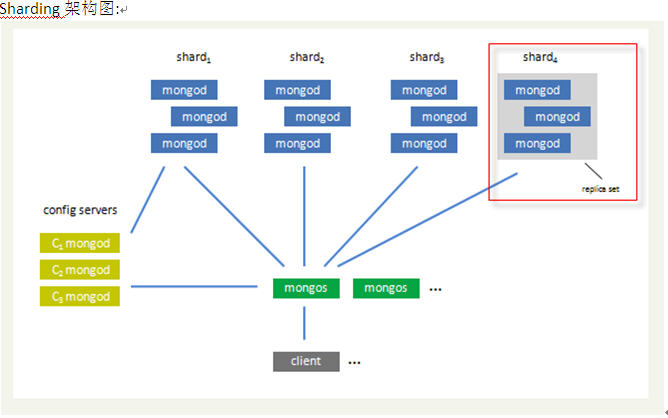
本例实际环境架构
本例架构示例图:

- 分别在3台机器运行一个mongod实例(称为mongod shard11,mongod shard12,mongod shard13)组织replica set1,作为cluster的shard1
- 分别在3台机器运行一个mongod实例(称为mongod shard21,mongod shard22,mongod shard23)组织replica set2,作为cluster的shard2
- 每台机器运行一个mongod实例,作为3个config server
- 每台机器运行一个mongs进程,用于客户端连接
| 主机 |
IP |
端口信息 |
| Server1 |
10.1.1.1 |
mongod shard11:27017
mongod shard12:27018
mongod config1:20000
mongs1:30000 |
| Server2 |
10.1.1.2 |
mongod shard12:27017
mongod shard22:27018
mongod config2:20000
mongs2:30000 |
| Server3 |
10.1.1.3 |
mongod shard13:27017
mongod shard23:27018
mongod config3:20000
mongs3:30000 |
软件准备
软件准备
1. 创建用户
groupadd -g 20001 mongodb
useradd -u 20001 -g mongodb mongodb
passwd mongodb
2. 安装monodb软件
su – mongodb
tar zxvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2.tar
安装好后,目录结构如下:
$ tree mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2
mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2
|– GNU-AGPL-3.0
|– README
|– THIRD-PARTY-NOTICES
`– bin
|– bsondump
|– mongo
|– mongod
|– mongodump
|– mongoexport
|– mongofiles
|– mongoimport
|– mongorestore
|– mongos
|– mongosniff
`– mongostat
1 directory, 14 files
3. 创建数据目录
根据本例sharding架构图所示,在各台sever上创建shard数据文件目录
Server1:
su – monodb
cd /home/monodb
mkdir -p data/shard11
mkdir -p data/shard21
Server2:
su – monodb
cd /home/monodb
mkdir -p data/shard11
mkdir -p data/shard22
Server3:
su – monodb
cd /home/monodb
mkdir -p data/shard13
mkdir -p data/shard23
配置relica sets
1. 配置shard1所用到的replica sets:
Server1:
cd /home/mongodb/mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2/bin
./mongod –shardsvr –replSet shard1 –port 27017 –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/shard11 –oplogSize 100 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/shard11.log –logappend –fork
Server2:
cd /home/mongodb/mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2/bin
./mongod –shardsvr –replSet shard1 –port 27017 –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/shard12 –oplogSize 100 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/shard12.log –logappend –fork
Server3:
cd /home/mongodb/mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2/bin
./mongod –shardsvr –replSet shard1 –port 27017 –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/shard13 –oplogSize 100 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/shard13.log –logappend –fork
初始化replica set
用mongo连接其中一个mongod,执行:
> config = {_id: ’shard1′, members: [
{_id: 0, host: ‘10.1.1.1:27017’},
{_id: 1, host: ‘10.1.1.2:27017’},
{_id: 2, host: ‘10.1.1.3:27017’}]
}
> rs.initiate(config);
同样方法,配置shard2用到的replica sets:
server1:
cd /home/mongodb/mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2/bin
./mongod –shardsvr –replSet shard2 –port 27018 –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/shard21 –oplogSize 100 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/shard21.log –logappend –fork
server2:
cd /home/mongodb/mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2/bin
./mongod –shardsvr –replSet shard2 –port 27018 –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/shard22 –oplogSize 100 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/shard22.log –logappend –fork
server3:
cd /home/mongodb/mongodb-linux-x86_64-1.7.2/bin
./mongod –shardsvr –replSet shard2 –port 27018 –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/shard23 –oplogSize 100 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/shard23.log –logappend –fork
初始化replica set
用mongo连接其中一个mongod,执行:
> config = {_id: ’shard2′, members: [
{_id: 0, host: ‘10.1.1.1:27018’},
{_id: 1, host: ‘10.1.1.2:27018’},
{_id: 2, host: ‘10.1.1.3:27018’}]
}
> rs.initiate(config);
到此就配置好了二个replica sets,也就是准备好了二个shards
配置三台config server
Server1:
mkdir -p /home/mongodb/data/config
./mongod –configsvr –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/config –port 20000 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/config.log –logappend –fork #config server也需要dbpath
Server2:
mkdir -p /home/mongodb/data/config
./mongod –configsvr –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/config –port 20000 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/config.log –logappend –fork
Server3:
mkdir -p /home/mongodb/data/config
./mongod –configsvr –dbpath /home/mongodb/data/config –port 20000 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/config.log –logappend –fork
配置mongs
在server1,server2,server3上分别执行:
./mongos –configdb 10.1.1.1:20000,10.1.1.2:20000,10.1.1.3:20000 –port 30000 –chunkSize 5 –logpath /home/mongodb/data/mongos.log –logappend –fork
#mongs不需要dbpath
Configuring the Shard Cluster
连接到其中一个mongos进程,并切换到admin数据库做以下配置
1. 连接到mongs,并切换到admin
./mongo 10.1.1.1:30000/admin
>db
Admin
2. 加入shards
如里shard是单台服务器,用>db.runCommand( { addshard : “<serverhostname>[:<port>]” } )这样的命令加入,如果shard是replica sets,用replicaSetName/<serverhostname>[:port][,serverhostname2[:port],…]这样的格式表示,例如本例执行:
>db.runCommand( { addshard : “shard1/10.1.1.1:27017,10.1.1.2:27017,10.1.1.3:27017″,name:”s1″,maxsize:20480} );
>db.runCommand( { addshard : “shard2/10.1.1.1:27018,10.1.1.2:27018,10.1.1.3:27018″,name:”s2″,maxsize:20480} );
注意:在添加第二个shard时,出现error:test database 已经存在的错误,这里用mongo命令连接到第二个replica set,用db.dropDatabase()命令把test数据库给删除然后就可加入
3. 可选参数
Name:用于指定每个shard的名字,不指定的话系统将自动分配
maxSize:指定各个shard可使用的最大磁盘空间,单位megabytes
4. Listing shards
>db.runCommand( { listshards : 1 } )
如果列出了以上二个你加的shards,表示shards已经配置成功
5. 激活数据库分片
命令:
> db.runCommand( { enablesharding : “<dbname>” } );
通过执行以上命令,可以让数据库跨shard,如果不执行这步,数据库只会存放在一个shard,一旦激活数据库分片,数据库中不同的collection将被存放在不同的shard上,但一个collection仍旧存放在同一个shard上,要使单个collection也分片,还需单独对collection作些操作
Collecton分片
要使单个collection也分片存储,需要给collection指定一个分片key,通过以下命令操作:
> db.runCommand( { shardcollection : “<namespace>”,key : <shardkeypatternobject> });
注:
a. 分片的collection系统会自动创建一个索引(也可用户提前创建好)
b. 分片的collection只能有一个在分片key上的唯一索引,其它唯一索引不被允许
One note: a sharded collection can have only one unique index, which must exist on the shard key. No other unique indexes can exist on the collection.
分片collection例子
>db.runCommand( { shardcollection : “test.c1″,key : {id: 1} } )
>for (var i = 1; i <= 200003; i++) db.c1.save({id:i,value1:”1234567890″,value2:”1234567890″,value3:”1234567890″,value4:”1234567890″});
> db.c1.stats()
{
“sharded” : true,
“ns” : “test.c1″,
“count” : 200003,
“size” : 25600384,
“avgObjSize” : 128,
“storageSize” : 44509696,
“nindexes” : 2,
“nchunks” : 15,
“shards” : {
“s1″ : {
“ns” : “test.c1″,
“count” : 141941,
“size” : 18168448,
“avgObjSize” : 128,
“storageSize” : 33327616,
“numExtents” : 8,
“nindexes” : 2,
“lastExtentSize” : 12079360,
“paddingFactor” : 1,
“flags” : 1,
“totalIndexSize” : 11157504,
“indexSizes” : {
“_id_” : 5898240,
“id_1″ : 5259264
},
“ok” : 1
},
“s2″ : {
“ns” : “test.c1″,
“count” : 58062,
“size” : 7431936,
“avgObjSize” : 128,
“storageSize” : 11182080,
“numExtents” : 6,
“nindexes” : 2,
“lastExtentSize” : 8388608,
“paddingFactor” : 1,
“flags” : 1,
“totalIndexSize” : 4579328,
“indexSizes” : {
“_id_” : 2416640,
“id_1″ : 2162688
},
“ok” : 1
}
},
“ok” : 1
}




